Quiz 1: Part A (30 pts)
README FIRST
For each example of each question you will be given the following format:
Example Format
--- Input ----
<Exact Input>
--- Output ---
<Exact Output>
Example: Addition Program
--- Input ----
3
7
--- Output ---
10
Code for Addition Program
# Python
a, b = int(input()), int(input())
print(a + b)
Some question, there may be a template for you. Copy and paste it, then write your code in there.
1. (5 pts) Warm-up
Write a program that takes 2 non-negative floating-point numbers as inputs: m and n.
The program shall output sum, absolute difference, product, mean, maximum, and minimum of those values. Round them to 2 decimal places
Input (Each Line)
- Integer m
- Integer n
Output (Each Line)
- Sum of m and n
- Absolute Difference of m and n
- Product of m and n
- Mean of m and n
- Maximum of m and n
- Minimum of m and n
Example 1
--- Input ----
4
10
--- Output ---
14.0
6.0
40.0
7.0
10.0
4.0
2. (5 pts) Prime
A prime number p is a number that only p and 1 can divide while p > 1.
Write a program that check if the integer that user inputs is a prime or not.
If p is prime, the program should output PRIME, otherwise NOT PRIME.
There are many methods to check whether the number is prime.
Input (Each Line)
- Integer p
Output (Each Line)
PRIMEorNOT PRIME
Example 1
--- Input ----
9
--- Output ---
NOT PRIME
Example 2
--- Input ----
17
--- Output ---
PRIME
3. (5 pts) Odds, Evens
Write a function that returns 2 numbers: how many odds and how many evens are there
in the list. The function takes a list x as an input and returns a and b.
Note that a function can return multiple values, and you can index them.
Template (Copy and paste)
# Template for Q1A 3
# Do not change anything else!
def count(x):
a, b = 0, 0
# write your code here
return a, b
exec(input().strip())
Example 1
--- Input ----
print(count([1, 3, 7, 9, 10, 2, 6, 3, 5, 7, 7, 9, 99]))
--- Output ---
(10, 3)
Example 2
--- Input ----
print(count([]))
--- Output ---
(0, 0)
4. (5 pts) Circular List
A circular list is a list that the index runs in circle. For an ordinary list of length 10, you can index them from 0 to 9. A circular list, on the other hand, can be indexed with any non-negative numbers.
For example, we have a circular list q = [0, 1, 2, 3] of length 4.
If we index them, we should get the following:
q[0] -> 0
q[1] -> 1
q[2] -> 2
q[3] -> 3
q[4] -> 0
q[5] -> 1
q[6] -> 2
...
q[61] -> 1
...
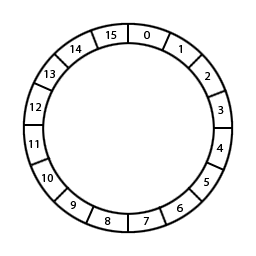
Circular Buffer (Ring Buffer) of size 16
How can we achieve this behavior? Write a function that takes 2 inputs:
a list q and an index i. The output should mimic q[i] as said above.
The list q is guaranteed to have at least 1 element.
Template (Copy and paste)
# Template for Q1A 4
# Do not change anything else!
def index(q, i):
# write your code here
# This function should return something.
exec(input().strip())
Example 1
--- Input ----
print(index([6, 9, 1, 2, 5, 7], 3))
--- Output ---
2
Example 2
--- Input ----
print(index([6, 9, 1, 2, 5, 7], 10))
--- Output ---
5
Example 3
--- Input ----
print(index([30], 9999999999))
--- Output ---
30
5. (10 pts) Time Difference
A point of time consists of hour: h, minute: m, and second: s.
Write a program that calculate the difference of time in this format.
The user should input h1, m1, s1 and h2, m2, s2
The program should output time difference in h m s format.
Conditions
- Time difference is absolute.
- 0 <= h <= 24
- 0 <= m, s <= 60
Template (Copy and paste)
# Template for Q1A 5
# Do not change anything else!
h1, m1, s1 = input().strip().split()
h2, m2, s2 = input().strip().split()
h1, m1, s1 = int(h1), int(m1), int(s1)
h2, m2, s2 = int(h2), int(m2), int(s2)
# write your code here
# Should print something.
Input (Each Line)
- Integers h1 m1 s1
- Integers h2 m2 s2
Output (Each Line)
- Time Difference in h m s format. See examples for more details.
Example 1
--- Input ----
24 00 50
24 00 30
--- Output ---
0 0 20
Example 2
--- Input ----
24 30 50
24 20 00
--- Output ---
0 10 50
Example 3
--- Input ----
24 00 00
23 50 50
--- Output ---
0 9 10
Example 4
--- Input ----
24 00 00
12 01 00
--- Output ---
11 59 0